Definition of the Polyurethane Rigid Foam Industry
Polyurethane rigid foam is made from rigid polyether polyols (commonly referred to as polyurethane rigid foam integrated polyether—white material) and polymer MDI (also known as black material) as primary raw materials. These materials undergo a specific foaming chemical reaction using dedicated molds. Depending on its properties, polyurethane rigid foam can be subdivided into soft foam, rigid foam, and semi-rigid foam. It is most commonly used to produce rigid polyurethane foam plastics, such as imitation wood furniture, interior decorative background walls, and ceiling trim lines. Additionally, polyurethane rigid foam has a wide range of applications in refrigerators, cold storage, spray coatings, solar energy, thermal pipelines, and construction.
Polyurethane rigid foam is a high-quality product with the following excellent characteristics: it is lightweight with high specific strength; it has a low thermal conductivity and effectively prevents vapor penetration; it features a closed-cell structure with a closed-cell rate of over 90%, offering excellent waterproof performance; it has exceptional insulation properties and is resistant to vibration, sound absorption, oil, and chemical corrosion. Moreover, the product has a fine particle size, high color quality, bright color, and good thermal stability. It is widely used in interior decoration, with varying quality levels, but it is relatively affordable and highly efficient. With continuous improvements in production technology and innovation, we are now able to manufacture a variety of products in different grades, with beautiful appearances, easy maintenance, moderate prices, and excellent abrasion resistance.
According to its actual application scenarios and the industries it serves, we classify it into rigid foam polyether polyols, imitation wood plastic polyether, cyclopentane-based rigid foam polyether, fully water-soluble polyether, and flame-retardant polyether with excellent fire resistance. Among these, imitation wood plastic polyether is widely used in manufacturing various imitation wood products; fully water-soluble polyether is mainly used for foaming processes in fully water pipelines; and flame-retardant polyether is used for producing products with high fire resistance requirements.
Characteristics of Polyurethane Rigid Foam
- Unique thermal insulation properties, high energy efficiency, and eco-friendliness.
- Lightweight, reducing load; excellent waterproof performance, combining insulation and waterproofing.
- Simple design, high efficiency, quick progress, good quality, and long service life.
- Fluorine-free foaming, adaptable to a wide range of environments.
- Strong adhesive ability, capable of bonding firmly to surfaces such as concrete, brick, wood, steel, asphalt, and rubber.
- Thermal conductivity: Can reach 0.017-0.022 W/m.k, lower than building insulation materials such as rock wool, glass wool, polystyrene boards, and extruded boards.
- Water repellency: Water repellency rate over 95%.
- Sealing performance: No cavities, no seams; completely wraps the building’s envelope structure, effectively preventing wind and moisture from flowing in and out of the building through gaps, achieving full sealing.
- Dimensional stability: Dimensional stability less than 1%, with a certain elastic deformation capability and an elongation rate greater than 5%.
- Consistent performance: Polyurethane is an inert material that does not react with acids or alkalis and is not a food source for insects or rodents, maintaining its properties and thermal insulation performance.
- Wind resistance: Compressive strength >300 Kpa, tensile strength >400 Kpa, strong wind resistance, and its foaming can penetrate wall gaps, increasing its shear resistance.
- Good combustibility: Self-extinguishes within 3 seconds of flame removal, surface carbonization prevents further combustion, and no molten drops are produced.
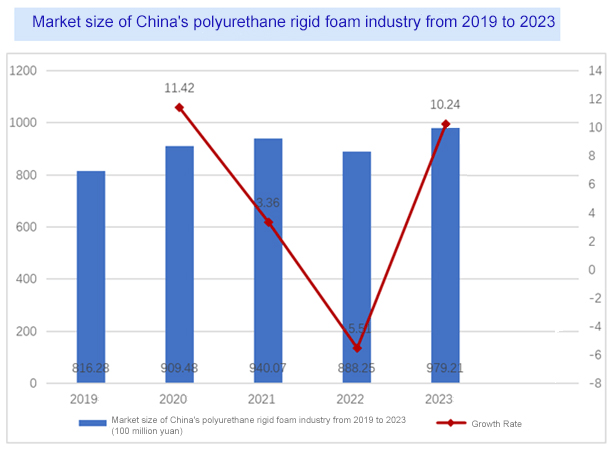
Industry Market Size
According to statistics, in 2019, the market size of the Chinese polyurethane rigid foam industry was 81.628 billion yuan, and by 2023, it had reached 97.921 billion yuan. The market size of the Chinese polyurethane rigid foam industry from 2019 to 2024 is as follows:
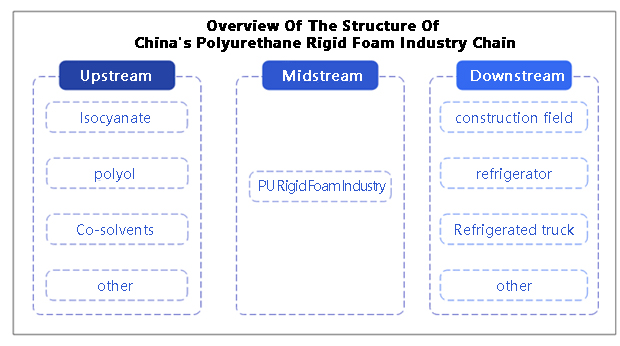
Industry Chain Structure of Polyurethane Rigid Foam
The upstream segment of the polyurethane rigid foam industry chain mainly involves the production of basic raw materials required for this polymer, with key components including isocyanates (such as MDI, TDI, etc.), polyols (covering both polyester and polyether polyols), and various solvents (such as DMF, methyl ethyl ketone, as well as stabilizers, flame retardants, etc.).
The midstream stage of the industry chain primarily includes the production and processing of polyurethane, which ultimately forms various product forms, such as polyurethane rigid foam. Due to its excellent insulation and waterproof properties, polyurethane rigid foam has found widespread applications in many fields, including construction and pipeline insulation. In particular, the building industry has seen extensive use of polyurethane rigid foam, such as in wall and roof insulation and waterproof spray foam, as well as pipeline insulation materials.
Analysis of Advantages in the Chinese Polyurethane Rigid Foam Industry
Lightweight and Superior Strength: Polyurethane rigid foam plastic is renowned for its lightweight, excellent specific strength, and exceptional dimensional stability. Notably, Japan has established standards for polyurethane rigid foam used in insulation applications, categorizing it into three types based on hardness. Due to its excellent mechanical strength, polyurethane rigid foam maintains its strength even in low-temperature environments and, in fact, performs better under such conditions. Its dimensional stability is outstanding, with minimal shrinkage observed. For example, when the rigid foam is placed in an environment at -20°C for 24 hours, its linear change rate remains below 1%.
Outstanding Insulation Performance: Polyurethane rigid foam is praised for its exceptional thermal insulation properties. The closed-cell structure of the foam has a content of over 90%, and the gas trapped within the cells exhibits extremely low thermal conductivity. This enables polyurethane rigid foam to provide excellent thermal insulation, even when the material is very thin, making it one of the best insulation materials in the construction industry.
Excellent Adhesion: Polyurethane rigid foam exhibits strong adhesive properties when bonding with metals such as steel, aluminum, stainless steel, as well as materials like wood, concrete, asbestos, asphalt, paper, and most plastics except polyethylene, polypropylene, and PTFE. It is especially suitable for making insulated profiles covered with various facings and as a potting material for electrical equipment’s insulation layers. Its excellent performance meets the growing demand for large-scale industrial production.
Exceptional Durability and Long Service Life: Polyurethane rigid foam has outstanding aging resistance and long-term insulation properties. Practical applications have proven that under the condition of undamaged outer skin, it can operate for up to 14 years at environmental temperatures ranging from -190°C to 70°C, demonstrating its exceptional aging resistance.
Excellent Flowability: The reaction products of polyurethane rigid foam possess excellent flowability, enabling easy filling into complex molds or spaces. Composites made from polyurethane rigid foam polymerization technology are lightweight, easy to assemble, and resistant to attracting insects or rodents, ensuring a long service life.
High Reactivity of Raw Materials: The raw materials required for polyurethane rigid foam have extremely high reactivity, enabling a rapid curing process. This allows for highly efficient and concentrated mass production in factory environments.
Future Development Trends in the Industry
“Low Carbon Economy” Focus: The “low carbon economy” is an economic development model centered around minimizing energy consumption, pollutant emissions, and environmental pollution. Guided by the principles of sustainable development, strategies like technological innovation, system reforms, industrial structure adjustments, and the development of new energy sources aim to reduce reliance on high-carbon energy sources like coal and oil. This shift reduces greenhouse gas emissions, creating a win-win situation for both economic development and environmental protection. The low carbon economy is critical for resolving the current energy crisis and promoting China’s industrial structure transformation and upgrading.
Key sectors such as power generation, industry, construction, and transportation are major sources of carbon dioxide emissions. To achieve energy conservation, emissions reduction, and low-carbon development, it is essential for China to promote low-carbon development both from the supply (e.g., renewable energy) and demand (e.g., low-carbon industry, low-carbon buildings, low-carbon transportation) sides. As a result, industries like solar energy and energy-efficient buildings are expected to experience significant growth, providing new momentum for the continued high-speed growth of the polyurethane rigid foam industry.
Rapid Development Driven by Solar Water Heater Applications: With global efforts to advocate energy conservation and reduce emissions in the context of a “low-carbon economy,” China is expected to maintain long-term optimism toward the policy support for solar thermal utilization. Since 2019, the Chinese government has fully supported the development of new energy infrastructure, including solar energy. This sector is promoted as a green, low-emission industry, with a series of laws and policies supporting the development and application of solar thermal technology.
Building Energy Efficiency Policies Driving Industry Growth: Building energy efficiency and carbon reduction have become key strategies for achieving carbon neutrality, and the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) and the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (MOHURD) have given significant attention to this. The recently published “Implementation Plan for Accelerating Energy Conservation and Carbon Reduction in the Construction Industry” outlines a comprehensive emission reduction strategy, including 12 key measures, with a clear target to ensure that by 2025, the share of electricity consumption in the building sector exceeds 55%. The successful implementation of this goal is vital for realizing China’s low-carbon economy.
Polyurethane rigid foam is an ideal material for building envelope insulation, attracting attention due to its excellent potential. Wall insulation has become a primary method for reducing building energy consumption, and the importance of insulation materials in the building energy-saving system is undeniable. Currently, insulation materials include extruded plastic boards, foam boards, spray-applied polystyrene, and polyurethane rigid foam. Polyurethane rigid foam, with its exceptional thermal insulation, mechanical strength, and waterproof properties, has firmly established itself as one of the top materials for the third generation of insulation materials. Additionally, flame-retardant polyurethane rigid foam automatically extinguishes and carbonizes in the event of a fire, effectively preventing the spread of flames, fulfilling the fire safety requirements of building insulation materials. As a result, polyurethane rigid foam has been widely used and promoted in residential building energy conservation, as well as in industrial buildings like cold storage and energy-efficient factories.
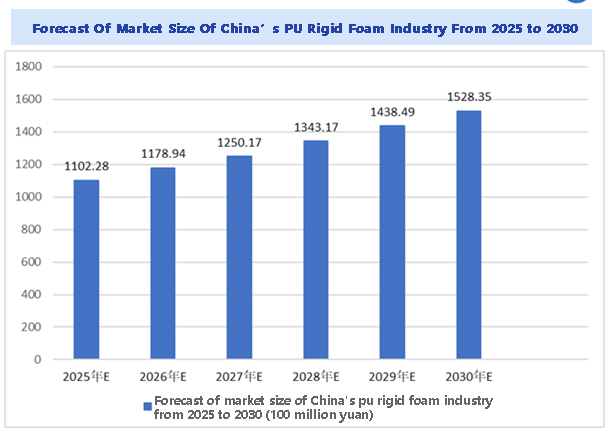
Industry Market Size Forecast
The market size of the Chinese polyurethane rigid foam industry is expected to steadily increase from 2024 to 2030, driven by growing market demand. By 2030, the market size is predicted to reach 152.835 billion yuan. The forecast for the Chinese polyurethane rigid foam industry market size from 2025 to 2030 is as follows: