The building insulation industry is an important part of the building materials industry. With the increasing global attention to energy efficiency and environmental standards, the building insulation materials market is experiencing rapid changes and growth. The following will provide a detailed analysis of the building insulation industry market, including the industry status, development trends, market share of major material types, market growth momentum and future prospects.
Current Status of Building Insulation Industry
The building insulation industry includes insulation materials used in building exterior walls, roofs, floors and other parts. Their main functions are to improve the energy efficiency of buildings, reduce energy consumption, improve comfort, and help reduce carbon emissions. With the increasing severity of global climate change and energy consumption issues, the building insulation industry has received more and more attention, especially in the field of green buildings and energy-saving buildings.
Market Size
Market size According to market research reports, the size of the global building insulation market in 2023 is about US$60 billion, and it is expected to reach US$90 billion by 2028, with a CAGR of about 8%. China, the United States, Europe and India are the main markets in the global building insulation market.
Market Drivers
Environmental regulations and policies: Many countries have implemented strict building energy efficiency standards and green building requirements, which has driven the demand for high-performance building insulation materials. For example, building energy efficiency regulations in Europe and the United States require new buildings to meet high standards of energy saving requirements.
Energy-saving demand: Building energy efficiency is increasingly becoming one of the key considerations in building design. Building insulation materials can significantly reduce building energy consumption and improve thermal comfort, especially in cold regions. The demand for insulation materials continues to grow.
Green buildings and sustainable development: With the global promotion of sustainable buildings and green buildings, building insulation materials, as the core part of green buildings, have shown a rapid growth trend in market demand. Green building certification systems (such as LEED, BREEAM, etc.) have also promoted the adoption of high-efficiency insulation materials.
Building decoration and renovation market: The demand for insulation materials is also increasing in old building renovation and refurbishment projects, especially in improving the energy efficiency and comfort of existing buildings.
Market Analysis of Building Insulation Materials
Building insulation materials can be divided into many types, the most common ones include polyurethane (PU), polystyrene (EPS), rock wool, glass wool, mineral wool, XPS (extruded polystyrene), etc. Different materials occupy different shares in the market due to their characteristics, application areas and prices.
Market Share and Analysis of Major Thermal Insulation Materials
Material type | Global market share (2023) | Average annual growth rate (CAGR) | Main advantages | Application areas |
Polystyrene(EPS) | 30%-35% | 3%-4% | Low cost, easy construction, good thermal resistance, but low fire resistance limits application | Residential, low-rise buildings, temporary buildings, low-cost buildings |
Polyurethane(PU) | 20%-25% | 6%-8% | Low thermal conductivity, excellent thermal insulation performance, good durability, especially suitable for high-end buildings | High-end residential, commercial buildings, cold chain logistics, energy-saving buildings, green buildings, etc. |
Rock wool | 15%-20% | 4%-5% | Excellent fire resistance, high temperature resistance, suitable for buildings requiring fire protection | High-rise buildings, industrial buildings, buildings with high fire protection requirements |
XPS(extruded polystyrene) | 10%-15% | 5%-6% | High compressive strength, moisture resistance, good thermal insulation performance | Underground buildings, roofs, exterior walls, cold storage, etc. |
Glass wool | 5%-7% | 2%-3% | Good sound insulation and fireproof performance, but poor thermal resistance performance | Sound insulation, heat insulation, commercial buildings, industrial buildings, projects with high fireproof requirements |
Mineral wool | 5%-7% | 2%-3% | High temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, suitable for special environments | Buildings in high temperature and chemically corrosive environments |
Regional Market Analysis of Insulation Industry
North America
North America (especially the United States) is one of the main markets for building insulation materials. The growth of the building insulation industry is driven by strict building energy efficiency regulations. The rapid development of the green building and energy-saving building markets in the United States has led to an increasing demand for high-performance insulation materials (such as polyurethane).
Europe
The European market, especially Germany, France and the United Kingdom, has continued to increase its demand for building insulation materials as building energy-saving standards continue to improve. EU regulations on building energy conservation have promoted the application of high-performance insulation materials such as polyurethane (PU), XPS and rock wool.
China
China’s building insulation market is growing rapidly. The Chinese government has introduced a series of policies to promote the development of green buildings and energy-saving buildings. In recent years, with the improvement of energy-saving and environmental protection requirements in the Chinese construction market, the market demand for polyurethane insulation materials has shown an upward trend, and the market share of polyurethane materials is expected to expand further.
Ấn Độ
India’s building insulation market is in a rapid development stage. With the growth of India’s economy and the expansion of the construction market, the demand for insulation materials is increasing. Especially in commercial and residential buildings, energy saving and green buildings have become new trends.
Polyurethane in Insulation Industry
Polyurethane is one of the most commonly used materials in the insulation industry due to its superior thermal performance, versatility, and durability. As a high-performance insulator, polyurethane is widely used for thermal insulation in a range of applications including buildings, appliances, industrial equipment, and transportation. Its low thermal conductivity and ease of application make it an ideal choice for improving energy efficiency and reducing heat loss.
Overview of Polyurethane in Insulation
Polyurethane insulation comes primarily in two forms:
- Rigid Polyurethane Foam (RPUF): This is the most common form of polyurethane used for insulation. It has a rigid structure and is often applied as insulation panels, boards, or spray foam.
- Spray Polyurethane Foam (SPF): This is a liquid form of polyurethane that expands upon application to form a solid foam, providing an airtight seal and excellent thermal insulation.
Properties of Polyurethane in Insulation
Polyurethane is favored in the insulation industry for its unique set of properties:
Low Thermal Conductivity: Polyurethane foam has one of the lowest thermal conductivities among common insulation materials, making it highly effective at reducing heat transfer.
- Thermal Conductivity (λ): Typically ranges from 0.020 to 0.030 W/m·K, depending on the formulation. This means it provides superior thermal insulation performance compared to materials like fiberglass and polystyrene.
High Insulating Efficiency: Polyurethane’s closed-cell structure traps air or other gases, which significantly reduces heat transfer. This makes it highly energy-efficient for both hot and cold environments.
Lightweight: Despite its high insulating properties, polyurethane foam is relatively lightweight, which makes it easy to handle, install, and transport.
Moisture Resistance: Polyurethane foam resists moisture absorption, preventing mold and mildew growth in buildings and other applications. This is particularly valuable in high-humidity environments.
Durability: Polyurethane foam is highly resistant to aging, weathering, and mechanical stress, ensuring it maintains its insulating properties over time. It also resists corrosion and rot, making it ideal for outdoor or industrial applications.
Sound Insulation: Polyurethane foam offers good acoustic properties, reducing sound transmission and improving the comfort of indoor spaces.
Flexibility and Formability: Polyurethane foam can be molded into various shapes, thicknesses, and densities, providing flexibility for a wide range of applications.
Applications of Polyurethane in Insulation
Polyurethane is used for insulation in a wide variety of industries, ranging from residential buildings to industrial systems. Its applications include:
Building Insulation
Wall Insulation: Polyurethane foam is commonly used for external and internal wall insulation. Rigid polyurethane foam boards (insulation panels) are typically installed between studs or applied directly to the exterior of buildings to improve thermal performance and reduce heating and cooling costs.
- External Insulation: It can be used as an external thermal insulation composite system (ETICS) for cladding purposes.
- Internal Insulation: Polyurethane spray foam is applied between walls and cavities for a seamless, airtight seal that enhances energy efficiency.
Roof Insulation: Polyurethane spray foam is commonly applied to flat or sloped roofs to prevent heat loss and improve the energy efficiency of the building. It also serves as a waterproofing layer.
- Advantages: Spray foam forms a continuous, seamless layer that prevents air leaks and moisture infiltration.
Floor Insulation: Polyurethane foam is also used to insulate floors, particularly in areas where temperature control is crucial, such as basements or garages.
Attic and Ceiling Insulation: Polyurethane foam provides excellent thermal insulation for attics and ceilings, preventing heat from escaping in winter and keeping homes cooler in summer.
Appliance Insulation
Polyurethane is widely used in the insulation of household appliances, particularly refrigeration and freezers, because of its excellent thermal insulating properties.
- Refrigerators and Freezers: Polyurethane foam is injected into the walls of refrigerators and freezers to create a high-performance insulating layer. The foam helps to maintain the internal temperature and reduce energy consumption.
- Water Heaters: Insulation of water heaters with polyurethane foam helps retain heat, reducing energy waste and improving efficiency.
Industrial Insulation
Polyurethane foam is used in various industrial applications to insulate pipes, tanks, and equipment, providing both thermal insulation and resistance to moisture and chemicals.
- Piping Insulation: Polyurethane foam is applied to industrial pipes, such as those used in oil, gas, and chemical industries, to reduce energy loss and maintain the temperature of the materials inside the pipes.
- Cold Storage: Polyurethane is used in the construction of cold storage units, such as warehouses for perishable goods, due to its ability to maintain low temperatures efficiently.
Transportation Insulation
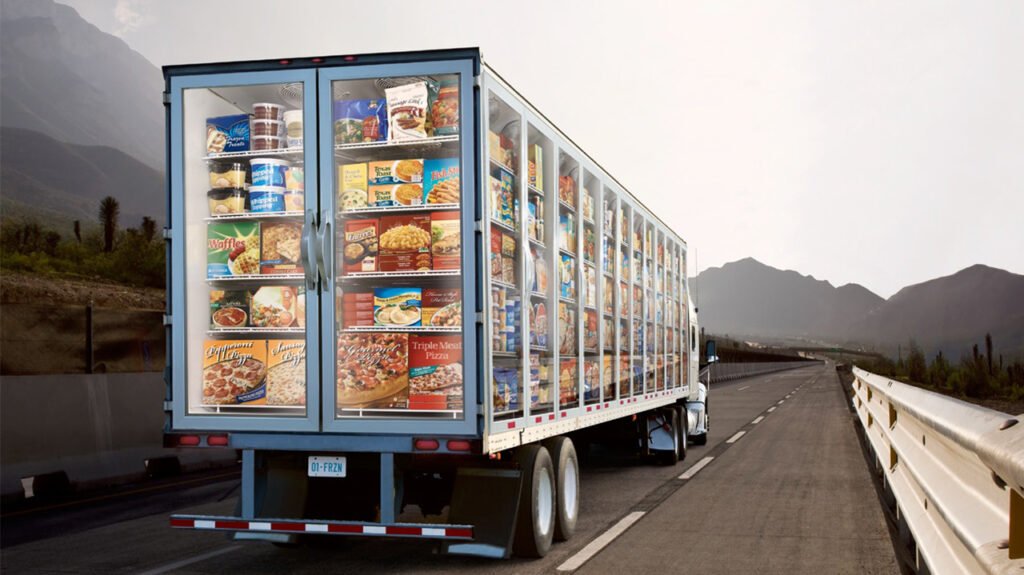
In the transportation sector, polyurethane is used for insulating refrigerated transport units and vehicles.
- Refrigerated Trucks and Trailers: Polyurethane foam is used to insulate the walls, floors, and roofs of refrigerated trucks and trailers, ensuring that temperature-sensitive goods can be transported at the correct temperature.
- Railcars and Shipping Containers: Similarly, polyurethane foam is used for insulating railcars and shipping containers used to transport perishable goods.
Specialized Insulation Applications
- Tank Insulation: Polyurethane foam is used for insulating tanks containing liquids that need to maintain a constant temperature, such as in the food processing and chemical industries.
- Cryogenic Insulation: Polyurethane foam can also be used in applications requiring very low temperatures, such as in the insulation of cryogenic tanks.
Benefits of Polyurethane in Insulation
- Energy Efficiency: One of the biggest advantages of polyurethane insulation is its ability to improve energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer. This is especially important in the context of reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling in buildings and homes.
- Cost-Effective: Although polyurethane foam may have a higher upfront cost compared to other insulation materials like fiberglass, its superior insulating properties often lead to long-term savings on energy bills.
- Space Efficiency: Because polyurethane provides superior insulation with a thinner profile compared to other materials, it allows more usable space within a building or structure.
- Airtight Seal: Polyurethane spray foam is particularly effective at sealing gaps, cracks, and seams, which helps to eliminate air leaks and improve the overall energy efficiency of buildings and appliances.
- Sustainability: Advances in polyurethane formulations have led to more eco-friendly options, including bio-based polyols (derived from renewable resources) and blowing agents that have a lower global warming potential (GWP).
Challenges and Considerations
While polyurethane is an excellent insulation material, there are some challenges and considerations:
- Environmental Concerns: The production of polyurethane typically involves the use of chemicals like isocyanates, which can be harmful to human health and the environment. However, manufacturers are working toward more sustainable production methods, including using bio-based materials and reducing the environmental impact of production processes.
- Fire Resistance: Polyurethane foam can be highly flammable. However, fire-resistant formulations are available, and additional fireproofing treatments can be applied to improve safety.
- Health and Safety: During the installation of spray polyurethane foam (SPF), proper precautions must be taken to avoid inhaling fumes or skin exposure, as the chemicals involved can be hazardous. It is important for professionals to follow recommended safety guidelines during application.
- Cost: Polyurethane foam insulation is often more expensive than fiberglass or cellulose, but the long-term energy savings and performance often justify the higher upfront cost.
Future Trends and Innovations
- Bio-Based Polyurethane: As demand for sustainable and eco-friendly materials grows, there is an increasing focus on developing bio-based polyols and polyurethane products that have a lower environmental impact.
- Improved Fire Resistance: With new innovations in flame-retardant chemicals, polyurethane foam is becoming safer for use in more fire-sensitive environments.
- Nanotechnology: Nanomaterials are being incorporated into polyurethane formulations to further enhance insulation properties, including improved fire resistance, moisture resistance, and overall thermal performance.
- Recyclable and Reusable Insulation: As part of the growing focus on sustainability, efforts are being made to develop more recyclable polyurethane foams, helping to reduce waste in the insulation industry.
Conclusion
Polyurethane is a highly effective insulation material that offers a range of benefits, including exceptional thermal performance, moisture resistance, durability, and flexibility. Its applications in building insulation, appliance insulation, industrial systems, and transportation are widespread. As the demand for energy-efficient and sustainable solutions continues to grow, polyurethane will remain a key material in the insulation industry, with ongoing innovations aimed at improving its performance, environmental impact, and safety.