What is Construction?
The construction industry is a large industry that involves the design, construction, maintenance and renovation of various buildings and infrastructure. The construction industry is not only an important part of the national economy, but also a core force driving urbanization, economic development and social change. It covers all aspects of infrastructure construction from residential, commercial and industrial buildings to roads, bridges, water conservancy facilities, etc. The healthy development of the construction industry directly affects many aspects of national economic growth, employment levels, resource consumption and environmental protection. With the changes in the global economy, the advancement of urbanization, the strengthening of environmental protection regulations and the continuous advancement of technology, the construction industry is facing many new opportunities and challenges.
The Composition of the Construction Industry
The construction industry is typically divided into several key segments:
- Residential Construction: This includes the construction of single-family homes, multi-family units, high-rise apartments, and villas.
- Commercial Construction: This category includes office buildings, shopping malls, hotels, and other commercial properties.
- Industrial Construction: This includes the construction of factories, warehouses, and distribution centers.
- Infrastructure Construction: This includes projects such as roads, bridges, railways, airports, and water infrastructure (e.g., dams, sewage systems).
- Public Buildings: This includes schools, hospitals, government buildings, and cultural institutions like museums and libraries.
Market Size and Growth Trends of Construction
According to a report by a market research agency, the global construction industry will have a market size of approximately $12 trillion in 2023, and it is expected that by 2028, the market size will be close to $15 trillion, with an average annual growth rate of 4%-5%. This is mainly driven by the global urbanization process, infrastructure construction needs, real estate development and environmental protection requirements.
Regional markets:
Asia Pacific: It is the largest market in the global construction market, especially in China and India where urbanization is accelerating and infrastructure construction continues to grow. In 2023, the construction market in Asia Pacific accounted for more than 50% of the global market share.
North America: The construction industry in the United States and Canada has grown steadily, especially in real estate development, public infrastructure and commercial buildings. The US market is expected to reach approximately $1.5 trillion by 2028.
Europe: The European construction market is affected by the slowdown in economic growth and environmental protection policies, but it still maintains a certain growth. It is expected that by 2028, the European construction market will reach $2 trillion.
Latin America and Africa: Despite the complex economic environment, the demand for infrastructure construction in these regions has gradually increased, and it is expected to maintain moderate growth in the future.
The construction industry is typically one of the largest sectors in any economy. It significantly contributes to GDP and employs millions worldwide. The global construction market has witnessed considerable growth over the years, driven by several factors:
- Real Estate Development: The real estate sector, especially residential and commercial building, has been a primary driver of construction demand. However, market conditions, such as fluctuations in housing prices or economic downturns, can significantly impact growth.
- Infrastructure Development: As urbanization continues globally, there is an increasing demand for infrastructure development, including roads, bridges, and utilities. In developing countries, there is a strong focus on expanding infrastructure to meet growing urban populations.
- Green Building and Sustainability: With increasing environmental concerns, there is a growing trend toward sustainable and energy-efficient buildings. Green construction practices, such as using environmentally friendly materials, energy-efficient systems, and reducing carbon footprints, are gaining importance.
- Technology and Innovation: Technological advancements are transforming the construction industry. Building Information Modeling (BIM), modular construction, and the use of automation and AI are improving efficiency and reducing costs. Additionally, 3D printing technology is beginning to play a role in construction innovation.
Challenges in the Construction Industry
Despite its growth, the construction industry faces a number of challenges:
- Labor Shortage and Rising Costs: The construction industry is highly labor-intensive, and there is often a shortage of skilled workers, which increases labor costs and delays project completion. Many regions are facing difficulties in attracting younger generations to construction trades.
- Fluctuating Material Costs: The price of construction materials such as steel, concrete, and lumber can be highly volatile, affecting project costs. Global supply chain issues, natural disasters, and geopolitical instability can all influence material prices.
- Regulatory and Environmental Compliance: Governments are increasingly imposing stricter environmental regulations, requiring builders to adopt green building practices, which can increase costs. Compliance with safety standards is also an ongoing challenge.
- Technology Adoption: While technological innovations hold great promise for the construction sector, many companies are still hesitant to adopt new technologies due to the high initial investment, resistance to change, and lack of skilled personnel to implement them.
- Risk Management: Construction projects often face risks such as accidents, budget overruns, delays, and unforeseen challenges during the building process. Effective risk management practices are crucial for mitigating these risks.
Polyurethane in Construction
Properties of Polyurethane in Construction
Polyurethane (PU) is a polymer made by reacting diisocyanates with polyols, and its properties can be customized based on the type and proportion of chemicals used. Some of the key properties of polyurethane that make it suitable for construction applications include:
- Thermal Insulation: Polyurethane has excellent thermal insulation properties due to its low thermal conductivity, making it a popular choice for insulation products.
- Durability: Polyurethane is resistant to wear and tear, making it suitable for high-traffic areas, coatings, and flooring.
- Moisture Resistance: It is highly resistant to moisture, making it ideal for use in areas that are exposed to high humidity or water.
- Flexibility: Polyurethane can be produced in rigid or flexible forms, allowing for a wide range of applications, from insulation boards to flexible sealants and coatings.
- Lightweight: Polyurethane is lightweight yet strong, making it easy to handle and install.
- Fire Resistance: Some formulations of polyurethane can be made fire-resistant, helping to meet building codes and regulations.
- Soundproofing: Polyurethane foam offers excellent soundproofing properties, making it useful in soundproofing applications in both residential and commercial construction.
Applications of Polyurethane in Construction
Polyurethane is used in various forms, including rigid foam, flexible foam, elastomers, and coatings, in the construction industry. Some of the key applications include:
Thermal Insulation
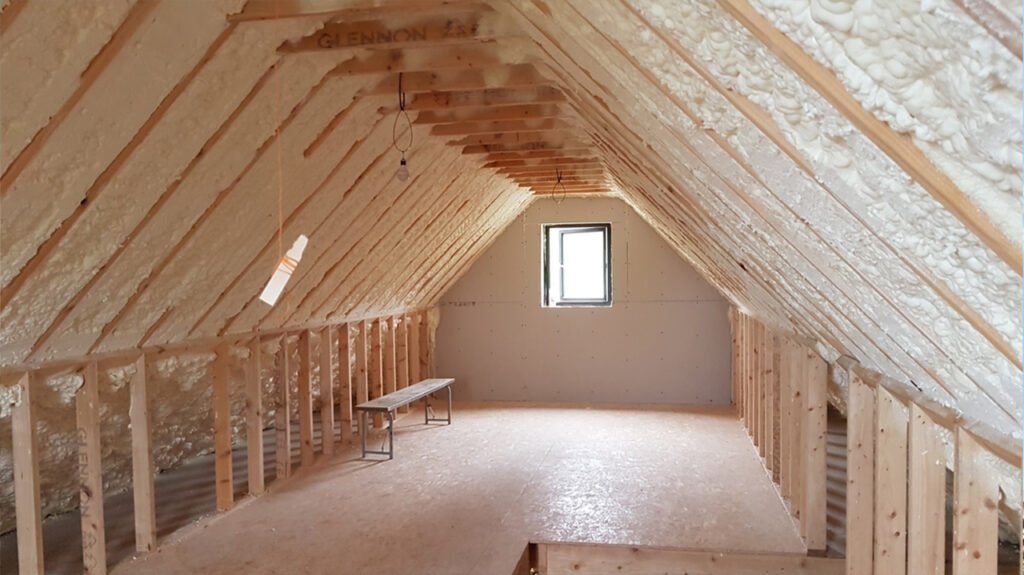
- Rigid Polyurethane Foam: One of the most common uses of polyurethane in construction is as a thermal insulator. Rigid polyurethane foam is known for its low thermal conductivity, making it highly effective at reducing heat transfer. It is used in insulation boards, spray foam insulation, and sandwich panels.
- Applications:
- Walls, roofs, and floorsin residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
- Cold storage facilities, such as freezers, refrigerated trucks, and food storage buildings.
- Pipeline insulationfor oil and gas industries.
- Applications:
- Spray Foam Insulation: Polyurethane spray foam is sprayed directly onto surfaces and expands to form an airtight seal. It is particularly useful for insulating irregularly shaped spaces, such as attics, crawl spaces, and walls with gaps.
- Benefits:
- Provides continuous insulation with no gaps or seams.
- Offers air and moisture barriers, which help prevent mold and mildew growth.
- Benefits:
Sealants and Adhesives
Polyurethane-based sealants and adhesives are commonly used in the construction industry due to their strong bonding capabilities, flexibility, and resistance to weathering and moisture.
- Applications:
- Window and door seals: Polyurethane sealants are used for sealing windows and doors to prevent air and water infiltration.
- Flooring adhesives: Polyurethane adhesives provide a strong bond for flooring materials, including hardwood, laminate, and tiles.
- Joint sealants: Used for sealing expansion joints, cracks, and seams in concrete or asphalt structures.
Coatings and Paints
Polyurethane coatings are widely used to protect surfaces from wear, chemicals, and UV radiation while providing aesthetic finishes. These coatings are particularly valued for their durability and resistance to abrasion and stains.
- Applications:
- Floor coatings: Polyurethane coatings are used on concrete, wood, and other types of flooring to provide a durable, easy-to-clean surface that withstands heavy foot traffic.
- Exterior and interior wall coatings: Polyurethane-based paints and coatings protect buildings from weathering and wear while offering a smooth finish.
- Protective coatings for steel and concrete structures: Polyurethane coatings help protect steel and concrete from corrosion, especially in harsh environments such as marine or industrial settings.
Soundproofing and Acoustic Insulation
Polyurethane foam is often used for soundproofing purposes in both residential and commercial buildings. Its ability to absorb and block sound makes it effective in improving indoor acoustics.
- Applications:
- Acoustic panelsfor walls and ceilings in offices, theaters, and recording studios.
- Floor soundproofing: Polyurethane foam underlayments help reduce noise transmission between floors in multi-story buildings.
Flooring Systems
Polyurethane-based flooring systems offer a range of benefits, including high resistance to chemicals, abrasion, and impact. These systems are commonly used in areas that require durable, easy-to-maintain flooring.
- Applications:
- Industrial floors: Polyurethane is used in warehouses, factories, and manufacturing plants where floors are exposed to heavy machinery, chemicals, and foot traffic.
- Sports facilities: Polyurethane coatings are often applied to sports courts and gymnasiums for their durability and smooth finish.
- Commercial kitchens: Polyurethane floors are easy to clean and resistant to grease, oils, and other substances commonly found in kitchens.
Waterproofing
Polyurethane-based waterproofing materials are widely used in construction to prevent water ingress in buildings and infrastructure.
- Applications:
- Roofing systems: Polyurethane coatings are used to provide a waterproof layer over roofs, especially in commercial and industrial buildings.
- Basements and foundations: Polyurethane membranes can be applied to basements and foundations to prevent water leakage.
Expansion Joints and Movement Control
Polyurethane is often used in the construction of expansion joints in concrete structures, such as bridges, highways, and buildings, to accommodate movement caused by temperature changes, vibrations, or settling.
- Applications:
- Bridge joints, parking structures, Và highwaysoften use polyurethane sealants to fill expansion joints and prevent water infiltration.
Spray Applied Polyurethane Foam (SPF)
Spray-applied polyurethane foam is used not only for insulation but also for other purposes such as:
- Soundproofingin walls, ceilings, and floors.
- Moisture controland prevention of mold growth in basements and crawl spaces.
Advantages of Polyurethane in Construction
Polyurethane’s wide range of applications offers many benefits to the construction industry:
- Energy Efficiency: As an excellent insulator, polyurethane helps reduce energy consumption by preventing heat loss and maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Polyurethane is a cost-effective material due to its durability, long lifespan, and efficiency in reducing heating and cooling costs.
- Moisture Control: Polyurethane helps control moisture, reducing the risk of mold, mildew, and structural damage from water.
- Versatility: Polyurethane can be customized to suit different applications, whether it’s in rigid foam, flexible foam, sealants, adhesives, or coatings.
- Durability: Polyurethane products are highly durable, resistant to abrasion, chemicals, and weather conditions, making them long-lasting.
- Sustainability: Some polyurethane products are manufactured with a focus on sustainability, including the use of recycled materials or low-emission processes.
Conclusion
Polyurethane plays an important and diverse role in the construction industry. Its excellent thermal insulation properties, durability, versatility, and resistance to moisture and chemicals make it an essential material for a wide range of applications, including insulation, coatings, adhesives, flooring, and soundproofing. However, the environmental and health concerns surrounding its production and use are prompting the industry to explore more sustainable and safer alternatives. As construction practices continue to evolve, polyurethane will remain a key material, with innovations in its formulation and application helping to meet the growing demand for energy-efficient, durable, and sustainable building solutions.