In the field of modern industrial manufacturing, polyurethane materials have become strategic materials in more than 20 industries such as automotive interiors, building insulation, and cold chain logistics due to their unique performance combination – excellent mechanical strength, excellent thermal insulation performance, and adjustable hardness range. According to statistics, the global market size of polyurethane products has reached $78 billion in 2023, with over 60% of products produced through high-pressure foaming technology. This breakthrough production method achieves precise mixing and instantaneous foaming of raw materials through a high-pressure environment of 20-150MPa. Compared with traditional low-pressure foaming technology, its product density uniformity is increased by 40%, and the closed cell rate can reach more than 95%.

The core value of high-pressure foaming technology is reflected in three dimensions: firstly, in terms of mixing efficiency, the high-pressure injection system can make the impact speed of isocyanate and polyol reach 120m/s, achieving sufficient reaction at the molecular level; secondly, through precise temperature control module (± 0.5 ℃) and closed-loop pressure control system, the foam rate fluctuation can be controlled within 3%; finally, the mixing head technology designed by Modularization shortens the time for equipment to switch between different formulations to 15 minutes, significantly improving the flexibility of the production line.

Understanding the working principle of the equipment plays a decisive role in the selection decision. Taking the metering system as an example, the flow accuracy of the plunger pump driven by the servo motor is 0.3% higher than that of the traditional gear pump, which is crucial for the production of A-grade surface products such as automobile dashboards. The self-cleaning function design of the mixing head can reduce the risk of cross-contamination between different batches to 0.02%, which has irreplaceable value for the production of medical-grade polyurethane products. When selecting equipment, it is necessary to combine the technical indicators of the product (such as bubble size requirements of 80-300μm), production rhythm (usually 30-90 seconds/mold), and raw material characteristics (such as the corrosiveness of flame retardants), and select equipment configuration with corresponding pressure levels (conventional 15-21MPa, precision molding requires more than 35MPa) and material compatibility.
Core working principle diagram
System flow (dynamic closed-loop system)
The polyurethane high-pressure foaming machine adopts a closed-loop control system, and the core process can be summarized as follows:
Raw material storage tank → High pressure metering pump → Constant temperature circulation pipeline → Mixing head dynamic injection → Mold forming → Finished product demouldingKey component linkage principle:
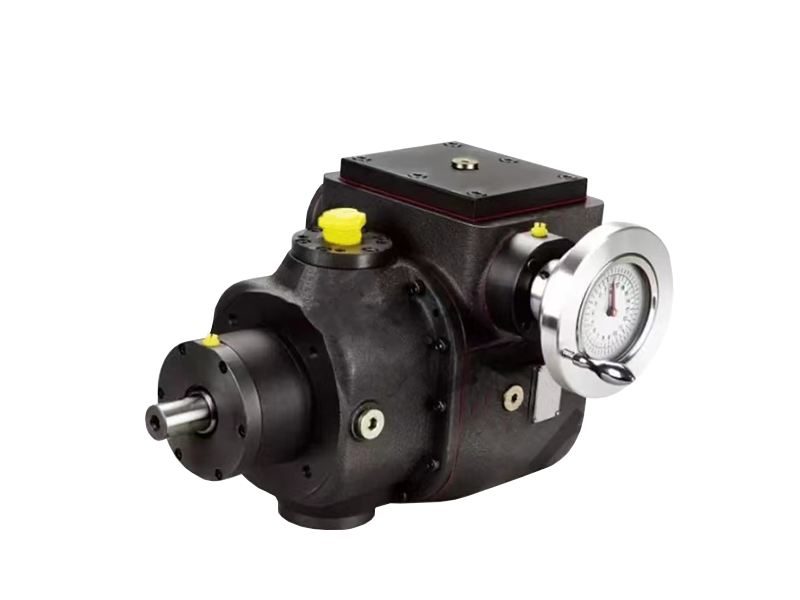

Two-component high-pressure pump
(A material isocyanate/B material polyol) independently conveys at a pressure ratio of ≥ 10:1

Self-cleaning mixing head
precise opening and closing within 0.2 seconds achieved by driving the valve stem with a servo motor

PID temperature control system
maintain the constant temperature of the raw material at 45 ± 1 ℃ (temperature deviation directly affects viscosity).
Three-stage work cycle (industrial-grade production rhythm control)
- Raw material preparation stage (Pre-Mixing)
- Raw material pretreatment: polyols need to be vacuum dehydrated to a moisture content of < 0.05%, and isocyanates need to be sealed with nitrogen to prevent moisture
- Measurement accuracy control: gear pump with mass flow meter achieves ± 0.5% ratio accuracy
- Temperature compensation mechanism: The heat transfer oil circulation system compensates for environmental temperature fluctuations to ensure that the viscosity is stable at 150-300mPa · s
- High Pressure Mixing Stage (High Pressure Impingement)
- Hybrid dynamics principle: At a pressure of 120-200 bar, two streams collide at a speed of 20-30 m/s
- Microscopic mixing process: pressure energy is converted into kinetic energy, generating a shear rate of > 5000s, achieving molecular-level mixing
- Residence time control: The special flow channel design of the mixing chamber compresses the material residence time to < 0.1 seconds to prevent pre-reaction
- Injection molding stage (Foaming & Curing)
- Pressure release effect: After the mixed material is injected into the mold, a sudden drop in pressure triggers physical foaming (N ÷ release).
- Mold cavity filling control: using multi-stage injection speed (0.5-5 L/s adjustable) to match complex cavity structures
- Crosslinking solidification management: The mold constant temperature system (40-80 ℃) is used with a release agent to achieve a 30-180 second release cycle
- Core technical parameters (process window control points)
Parameter category | Typical range | Process influence dimension | Application scenario examples |
Mixing pressure | 120-200bar | Pressure ↑ → Mixing uniformity ↑/Pore diameter ↓ | Car dashboard (150bar) |
Pressure ↓ → Equipment wear ↓/Energy consumption reduction | Building insulation board (120bar) | ||
Discharge accuracy | ±0.8%-1.5% | An accuracy deviation of > 2% will result in a density fluctuation of > 5%. | Refrigerator door foaming (± 0.8%) |
Injection speed | 0.5-5 L/s (Segmented) | Speed ↑ → Fully filled but easily trapped | Complex structural components (3-stage variable speed) |
Speed ↓ → Good surface quality but reduced efficiency | Appearance parts (constant speed 1.2L/s) | ||
Temperature control accuracy | ±1℃ | Temperature ↑ 1 ℃ → Reaction rate increased by 15-20% | Winter environment (compensation + 3 ℃) |
Material ratio control accuracy | ±0.5% | Deviation > 1% will result in a hardness change of > 10 Shore | High rebound foam (± 0.3%) |
Operating notes:
- Before production, it is necessary to perform three or more air circulations to discharge pipeline bubbles
- The cleaning cycle of the mixing head should not exceed 8 hours of continuous operation
- When the environmental humidity is > 70%, the raw material dehumidification system must be started
- The injection pressure curve should match the mold exhaust design (it is recommended to reserve 0.3-0 mm exhaust clearance)
Disassembly of equipment core components
High-pressure metering system
1. Functional positioning
High-precision fluid metering core unit, suitable for quantitative output control of viscous media (such as adhesives, resins), metering accuracy can reach ± 0.5%, working pressure range 0.1-40 MPa.
2. Structural disassembly
High-pressure plunger pump unit: using ceramic-coated plungers, equipped with dual redundant pressure sensors
Buffer stabilizing device: three-stage buffer tank + pulsating damper structure
Flow monitoring module: Coriolis mass flowmeter + laser particle size analyzer combined
3. Design points
Pulsation suppression: By designing a three-pump structure with a phase difference of 120 °, flow fluctuation < 2% is achieved
Self-cleaning design: Integrated backwash channel to prevent media crystallization blockage
Overload protection: The intelligent unloading valve automatically opens for protection when the pressure exceeds the limit
2. Structural disassembly
High-pressure plunger pump unit: using ceramic-coated plungers, equipped with dual redundant pressure sensors
Buffer stabilizing device: three-stage buffer tank + pulsating damper structure
Flow monitoring module: Coriolis mass flowmeter + laser particle size analyzer combined
3. Design points
Pulsation suppression: By designing a three-pump structure with a phase difference of 120 °, flow fluctuation < 2% is achieved
Self-cleaning design: Integrated backwash channel to prevent media crystallization blockage
Overload protection: The intelligent unloading valve automatically opens for protection when the pressure exceeds the limit


Mixing spray device
1. Function implementation
Achieve precise mixing of multi-component (2-6 types) materials, with a mixing uniformity of > 98% and support for online viscosity adjustment.
2. Core composition
Static mixing unit: spiral blade mixing chamber (replaceable design)
Dynamic injection module: porous atomizing nozzle (aperture 0.1-0 adjustable)
Pressure balance system: including back pressure regulating valve and pressure compensator
3. Key technologies
Laminar flow mixing technology: Reynolds number control < 2000 ensures laminar flow state
Anti-drip design: double cut-off solenoid valve + negative pressure recovery device
Self-adaptive adjustment: automatically adjust the length of the mixing chamber based on flow feedback
Temperature control system
1. System architecture
Dual-channel independent temperature control system (medium channel/equipment channel), temperature control accuracy ± 0.3 ℃, response time < 15s.
2. Functional modules
Heating/cooling unit: semiconductor TEC module + auxiliary resistance heating
Heat exchanger: plate-fin structure, heat transfer efficiency ≥ 85%
Temperature field monitoring: 16-point distributed PT100 sensor array
3. Control strategy
PID parameter self-tuning: automatically optimize control parameters based on medium characteristics
Thermal inertia compensation: Establish equipment heat capacity model for predictive adjustment
• Safety protection: three-level overheating protection (software alarm → hardware power failure → physical fuse)
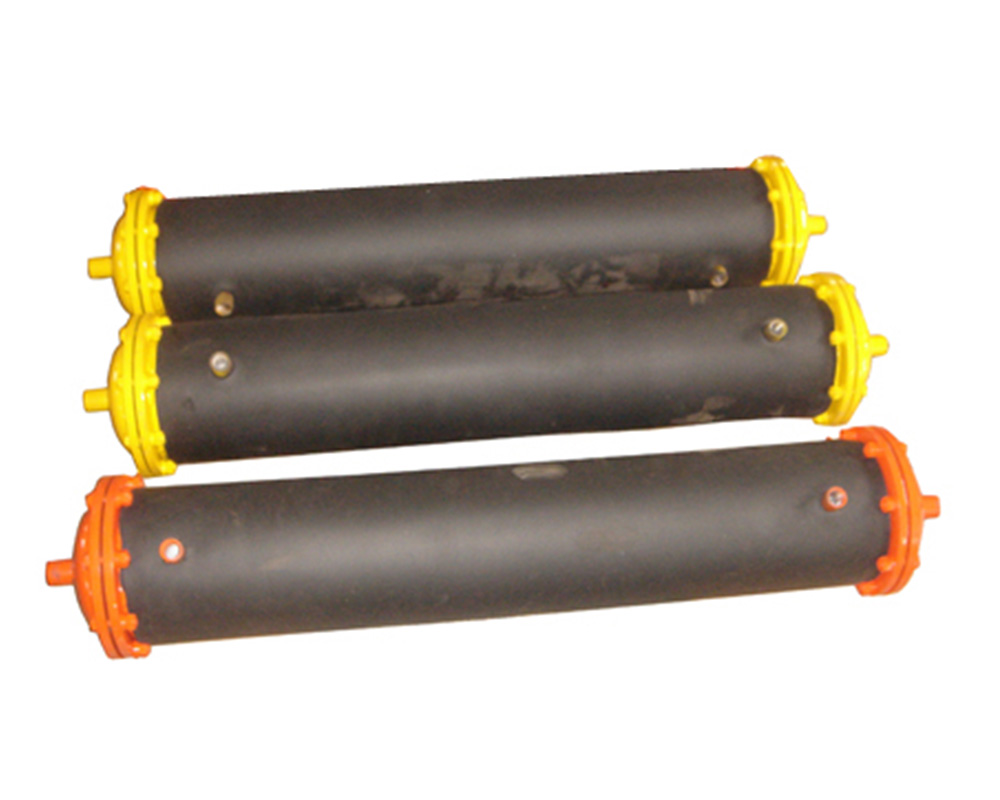


PLC control system
1. System composition
Main control unit: Dual CPU redundant architecture (SIL3 security level)
IO module: supports 32 AI/64 DI channels
HMI interface: 10.1-inch industrial touch screen (IP65 protection)
2. Core features
Formula management: Supports storage of 200 sets of process parameters
Motion control: 8-axis linkage control (± 1μm positioning accuracy)
Fault diagnosis: 500 + fault code libraries, supporting fuzzy reasoning diagnosis
3. Communication integration
Industrial bus: PROFINET + EtherCAT dual protocol compatibility
Data interface: OPC UA + MQTT dual protocol support
Remote maintenance: 4G/WIFI dual-mode communication module (AES256 encryption)
System integration advantages:
- Modularization design: support independent maintenance/replacement of each subsystem
- Energy efficiency optimization: standby power consumption < 50W, operating energy efficiency ratio ≥ 3.8
- Expansion capability: reserve 20% IO interface and 30% program capacity
- Compliance: Through CE, UL, GB5226.1 and other multiple certifications
Comparison of technical advantages
Analysis of Core Technology of High Pressure Foaming Machine VS Low Pressure Foaming Machine
In the field of polyurethane material production, the choice of equipment pressure system directly affects product quality and production efficiency. Our independently developed high-pressure foaming machine demonstrates significant advantages in the following core parameters.
1. Hybrid efficiency revolution (60-200bar VS 5-20bar)
The high-pressure system achieves nano-level mixing of polyols and isocyanates at a supercritical state of 200 bar through precision metering devices, with a mixing uniformity of 99.2% (industry average of 86%). This molecular-level mixing effectively eliminates common “stripe defects” in low-voltage equipment, especially suitable for fields with strict requirements for pore structure such as car seats and refrigerator insulation layers.
2. Breakthrough in finished product performance
Under the same MDI dosage, the closed-cell rate of products formed by high-voltage equipment is increased to 92% (78% for low-voltage equipment), and the thermal conductivity is reduced by 0.008W/(m · K). This means that the insulation time of the cold chain logistics box can be extended by 3-5 hours, and the protective layer of the new energy vehicle battery pack can be reduced by 15% while maintaining the same insulation performance.
3. Intelligent production iteration
Equipped with a patented dynamic pressure compensation system, the response speed reaches 0.03 seconds/time (traditional equipment 0.5 seconds). Under continuous production conditions, the fluctuation range of product density is controlled within ± 1.5% (industry standard ± 5%). With the AI visual inspection module, precise control of bubble diameter tolerance ± 5μm is achieved.
Deepening application scenarios
Against the backdrop of the rapid development of new energy vehicles, material applications are driving breakthroughs in three core technologies.
- Body lightweight solution: Honeycomb polyurethane foam (density only 0.3g/cm ³) replaces traditional metal brackets, helping Tesla Model Y reduce weight by 18% and increase endurance by 12%.
- Breakthrough in battery thermal management: The application of aerogel insulation sheet (thermal conductivity coefficient 0.018W/m · K) in CATL battery packs has increased the thermal runaway delay time from 3 minutes to 20 minutes
- NVH Performance optimization: BASF’s sound-absorbing cotton material reduces in-car noise by 6dB, equivalent to converting urban traffic environments to library silence levels
Typical application: The BYD Seal model uses three-layer composite sound insulation materials, and the interior noise is only 63 decibels at a speed of 120km/h, which is 22% lower than that of the same level of fuel vehicles

Cold chain insulation applications: a precision revolution in temperature control
Cold chain technology is upgrading from “cold preservation” to “intelligent temperature control”.
- Refrigerated truck technology iteration: Vacuum insulation board (VIP) reduces the thickness of the 8.6-meter refrigerated truck box by 40%, increases the plot ratio by 15%, and reduces energy consumption by 30%.
- Breakthrough in pharmaceutical cold chain: Phase change materials (PCM) achieve a constant temperature of 2-8 ℃ for 72 hours during COVID-19 vaccine transportation, and the breakage rate decreases from 3% to 0.2%.
- Green logistics solution: JD.com logistics uses aerogel cold storage plates, and the temperature fluctuation in the warehouse is controlled within ± 0.5 ℃, reducing energy consumption costs by 40%.
Technical comparison: The R value (thermal resistance value) of traditional polyurethane foam materials is 5.6, while the R value of new nano-aerogel materials is 10.2, and the insulation efficiency is increased by 82%.

Technological evolution trend
1. Multifunctional integration: The sound insulation material of the BMW iX model also has electromagnetic shielding function
2. Intelligent response materials: the application of shape memory polymers in cold chain packaging to achieve temperature self-regulation
3. Sustainability breakthrough: BASF bio-based polyurethane foam carbon footprint reduced by 60%
The data shows that from 2020 to 2025, the compound growth rate of new insulation materials in the field of new energy vehicles reached 28.6%, and the penetration rate in the field of pharmaceutical logistics increased from 12% to 39%, verifying the broad prospects of technological applications.
Equipment Selection Guide
Key selection parameter table and decision logic
(Table 1: Core parameter system for general equipment selection)
Parameter category | Key metrics | Selection advice | Examples of Industry Differences |
Performance parameters | Processing capacity (tons/hour) | Select according to 120% of peak demand, taking into account flexible production needs | Food processing needs to consider the ability to switch between multiple varieties |
Accuracy level (μm) | Choose according to the 80% accuracy required by the process, leaving room for technical upgrades | Semiconductor equipment requires ± 0.5μm level control | |
Energy efficiency indicators | Unit energy consumption (kW · h/unit output) | Referring to the first-level indicators of national energy efficiency standards, the Payback Period is controlled within 3 years | Injection molding machines need to pay attention to the energy saving rate of the servo system |
Thermal efficiency (%) | Industrial boilers should be ≥ 94%, and the ROI of waste heat recovery systems should be ≤ 2 years | Chemical reaction equipment needs to integrate thermal coupling design | |
Structural parameters | Material grade (stainless steel/special steel) | Choose 316L grade for food and medical treatment, and choose Inconel alloy for high temperature environment | Marine engineering equipment must meet NACE MR0175. |
Protection level (IPXX) | Conventional workshop IP54, dust environment IP65, underwater components IP68 | Pharmaceutical clean areas must comply with GMP sealing standards | |
MTBF (mean interval between failures) | Key equipment ≥ 10000 hours, supporting predictive maintenance system | Automotive production lines require a 99.5% operating rate | |
Modularization design | The core unit adopts a quick disassembly structure, and the maintenance window is ≤ 4 hours | Mining machinery requires the ability to replace quickly in the field |
Selection decision model:
Basic requirements → process matching analysis → full life cycle cost accounting → supplier technical evaluation → practice run verification
In-depth analysis and optimization strategies for maintenance costs
(Maintenance cost composition model)
Total Cost Of Carry (TCO) = Acquisition Cost × 0.3 + (Annual Maintenance Fee × Equipment Years) × 1.2 + (Downtime Loss × Failure Rate) + Energy Consumption × Service Life + Residual Value Treatment Cost
Maintenance cost optimization path:
- Construction of preventive maintenance system
- Establish a maintenance plan based on RCM (reliability-centered maintenance)
- Key component replacement cycle is associated with MTBF management
- Implementation of condition monitoring (vibration analysis + oil detection + infrared thermal imaging)
- Spare parts inventory intelligent management
- ABC classification method: JIT procurement is implemented for Class A spare parts (10% of the category accounts for 70% of the value)
- Establish a regional shared spare parts warehouse, and increase inventory Turnover Ratio by 40%.
- Implement standardized transformation, and increase the proportion of common parts to 60%.
- Energy efficiency continuous improvement
- Installation of smart meters for energy efficiency base line measurement
- Implement energy-saving transformation of motor system (frequency conversion + permanent magnet technology)
- Waste heat recovery system integration reduces energy consumption by 15-25%.
- Digital maintenance transformation
- Deployment of CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System)
- Application of AR remote assistance technology to shorten fault diagnosis time
- Prediction of Spare Parts Failure Cycle Based on Big data
Typical case analysis:
A certain auto parts company implemented selection optimization.
- Stamping equipment selection increases servo drive system, reducing energy consumption by 38%
- Using Modularization injection molding unit, the mold change time is shortened by 65%.
- After deploying predictive maintenance, unplanned downtime is reduced by 42%.
- Total Cost Of Carrying Three Years Down 19.7%
Implementation of recommendations
- Establish XFN selection committee (technical/production/financial)
- Develop equipment lifecycle management process documents
- Carry out supplier joint research and development (JVD) cooperation
- Regular equipment health assessment audits
FAQ
1. The core difference between polyurethane high-pressure foaming and traditional processes
Core logic: Solve users’ questions about the value of process upgrade through technical comparison.
Professional answer: There are significant differences between high-pressure foaming and traditional low-pressure foaming processes in mixing methods, reaction efficiency and finished product quality:
- Mixing method: high-pressure foaming adopts precision metering pump (error ≤ ± 1%) and dynamic mixing head to achieve high-speed impact mixing of raw materials (pressure can reach 150-200bar), while traditional technology relies on mechanical stirring, and the mixing uniformity is poor.
- Reaction control: The high-pressure process precisely regulates the reaction temperature through a closed-loop temperature control system (± 1 ℃ accuracy) to avoid problems such as uneven foaming and contraction caused by temperature fluctuations in traditional processes.
- Finished product performance: The foam closed cell rate of high-pressure foaming can reach more than 95% (the traditional process is only 80% -85%), the thermal insulation performance and mechanical strength are increased by 30% -50%, and there is no bubble delamination phenomenon.
- Environmental protection: high-voltage equipment to achieve 100% utilization of raw materials, no drip waste, VOC emissions reduced by more than 60%.
User value: Help companies evaluate the energy-saving and efficiency-enhancing space after technology upgrades, and clarify the return on investment (ROI).
2. What preconditions are required for device startup
Core logic: Ensure user compliance and avoid equipment failure or production accidents due to insufficient preparation.
Professional answer: Before starting the high-pressure foaming equipment, the following 5 key checks need to be completed:
- Environmental inspection: the workshop temperature should be stable at 20-30 ℃ (± 2 ℃), humidity ≤ 65%, to prevent moisture absorption or crystallization of raw materials.
- Raw material preparation: The ratio of isocyanate (black material) and combined polyether (white material) is strictly set according to the process card (error < 0.5%), and the raw materials need to be stored at a constant temperature for 24 hours in advance (25 ± 2 ℃).
- Parameter settings: Confirm the injection pressure (120-180bar), discharge (200-800g/s), cleaning cycle (automatic flushing every 30 minutes) and other parameters in the HMI interface to match the product process.
- Equipment preheating: Before starting, it is necessary to run without load for 10-15 minutes to ensure that the temperature of A/B material pipe reaches 40 ± 1 ℃ and the mixing head temperature is 55 ± 1 ℃.
- Safety confirmation: Check the emergency stop button, pressure sensor, explosion-proof valve status, the operator needs to wear chemical protective clothing, goggles and air supply respirator.
User value: Standardized operating procedures can reduce more than 70% of equipment startup failures and ensure continuous production stability.
3. How to deal with common blockage problems
Core logic : Provide quick diagnosis and emergency plan, reduce downtime loss.
Professional answer:
Causes and solutions for material blockage:
- Raw material impurity blockage: Install a 100-mesh filter at the outlet of the material tank and clean the filter screen every shift. If it is blocked, immediately switch to the backup pipeline and use a special cleaning agent (such as DOP solvent) to backwash the mixing head.
- Proportional imbalance: Check the gear wear of the metering pump (wear amount > 0.1mm needs to be replaced), monitor the A/B material output in real time through the flowmeter, and automatically alarm and stop when the deviation exceeds 2%.
- Abnormal temperature: When the material temperature is below 35 ℃, isocyanate will crystallize. A backup heating belt should be used, and the heating rate should be controlled at 3 ℃/min to avoid local overheating and carbonization.
- Nozzle blockage: After disassembling the mixing head, treat it with an ultrasonic cleaner (40kHz) for 30 minutes. Stubborn residues can be mechanically removed after freezing with liquid nitrogen.
Preventive measures:
- Perform 3 automatic flushing procedures after daily production (pressure adjusted to 250 bar to flush residue).
- Monthly sealing testing of proportional valves and check valves (allowable leakage < 0.5ml/min)
- Operator training assessment “three inspection methods”: check pressure curve, check mixing effect, check finished foam structure
User value: Through systematic solutions, the processing time of material blockage fault is shortened from 2 hours to less than 15 minutes, and the annual waste loss is reduced by more than 200,000 yuan.